Gate valve
Release time:
01 Feb,2025
I. Overview:
Gate valves, as one of the indispensable important equipment in modern industry, play a crucial role in various industrial pipelines. Their main characteristics include large opening, small flow resistance, good sealing performance, convenient operation, and long service life. They are widely used in petrochemical, automation control, energy, and construction fields. Their excellent performance and reliability provide strong support for production operations and have made positive contributions to national economic development.
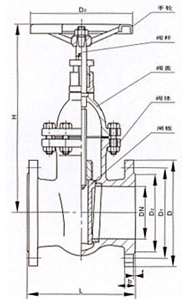
II. Gate Valve Structure
Gate valves are mainly composed of the following parts:
Valve body: Generally rectangular or square, with a central passage inside, and two interfaces on both sides for connection to the pipeline.
Gate: As the valve's switching component, its shape is the same as the valve body, suspended in the valve body, controlling the flow rate of the fluid in the pipeline by moving up and down.
Valve seat: The sealing component of the valve, commonly made of copper, stainless steel, etc. When the gate contacts the valve seat, the sealing gasket is sandwiched between them, forming a sealed environment and ensuring the gate valve's sealing performance.
Valve stem: An important component connecting the valve and the operating device, generally made of stainless steel.
Operating device: Includes manual and electric devices for controlling the opening and closing of the gate.
III. Gate Valve Working Principle:
The opening and closing process of a gate valve is achieved through friction between the gate and the valve seat. When the valve is closed, the gate moves down and tightly fits the valve seat, thus blocking the pipeline; when the valve is opened, the gate rises and separates from the valve seat, making the pipeline unobstructed. This switching method gives the gate valve the characteristics of low flow resistance and good sealing performance.
IV. Types of Gate Valves
According to the movement form, gate valve stems are divided into rising stem (lifting shaft) and non-rising stem (rotating shaft), and gate valves are therefore divided into rising stem gate valves and non-rising stem gate valves.
- Rising stem gate valve

The handwheel (or other driving device) is fixed on the valve stem nut. When the handwheel (or other driving device) rotates, it drives the valve stem nut to rotate, and the valve stem moves up and down, thus driving the gate valve to rise and fall to open and close the pipeline. When the rising stem gate valve is opened, the valve stem extends from above the handwheel, directly showing the opening degree of the gate valve. The trapezoidal thread of the valve stem is in the upper half of the valve stem, which does not directly contact the medium and is not corroded by the medium, and is also easy to lubricate. Therefore, it is suitable for gate valves with corrosive media, dirty media, and high-temperature steam media. The opening and closing degree of the valve can be directly seen from the thread, which is also one of its advantages. The disadvantage is that, due to the exposed thread, it is easy to stick to dust in the air, accelerating thread wear, so it should be installed indoors as much as possible. Despite this, its application is still widespread.
2. Non-rising stem gate valve
The handwheel (or other driving device) is fixed on the valve stem, and the valve stem thread is fixed on the top of the gate. When the handwheel (or other driving device) rotates, the valve stem thread drives the gate to move up and down. The valve stem can only rotate. The advantage is that the valve stem does not rise when opened, and the required installation space is smaller. Therefore, it is often used as a large-passage gate valve or in situations where installation space is limited. Since the valve stem does not move up and down, it cannot show the opening degree like the rising stem gate valve by the length of the valve stem extension, so an opening indicator should be installed. Because the threaded part of the valve stem and the valve stem nut of the non-rising stem gate valve are in contact with the medium inside the valve cavity, they are easily corroded by the medium, and the valve stem thread is difficult to lubricate. The valve body and valve cover are mostly flange-connected. The medium passage in the valve body is mostly cylindrical or other equal-section shapes. For gate valves with larger diameters, a valve seat with a reduced section is also used, that is, the passage gradually shrinks, and after passing through the valve seat, it gradually expands. Its advantages are:
(1) The size of the valve parts is reduced, the weight is reduced, and materials are saved. The sealing surface is reduced, and the amount of fine processing is reduced.
(2) Due to the reduction in the size of the gate, the force acting on the gate is reduced, and the opening and closing force of the gate valve is correspondingly reduced.

Z45T—10、Z45T—16Q type non-rising stem wedge single gate valve
Manual, flange connection, non-rising stem wedge rigid single gate, valve seat sealing surface material bronze, nominal pressure PN10~PN16, gate valve with valve body material of gray cast iron (Z45T—10) and ductile iron (Z45T—16Q).
Main parts materials of Z45T-10 manual gate valve:
| Model |
Valve body, valve cover, gate |
Sealing ring |
Valve stem |
Packing |
| Z45H-10 |
Gray cast iron, cast steel |
Stainless steel |
Carbon steel, stainless steel |
Oil-impregnated packing |
Z45T-10 manual non-rising stem cast iron gate valve dimensions
| DN |
L |
D |
D1 |
D2 |
Z-Фd |
H |
| 50 |
178 |
165 |
125 |
102 |
4-Ф19 |
285 |
| 80 |
203 |
200 |
160 |
138 |
8-Ф19 |
330 |
| 100 |
229 |
220 |
180 |
158 |
8-Ф19 |
405 |
| 125 |
254 |
250 |
210 |
188 |
8-Ф19 |
460 |
| 150 |
267 |
285 |
240 |
212 |
8-Ф23 |
506 |
| 200 |
292 |
340 |
295 |
268 |
8-Ф23 |
610 |
| 250 |
330 |
395 |
350 |
320 |
12-Ф23 |
730 |
| 300 |
356 |
445 |
400 |
370 |
12-Ф23 |
950 |
V. Electric Gate Valves
Electric gate valves control the opening and closing of the valve core through an electric actuator, thus achieving the cut-off or passage of pipeline fluid.
1. Automated control: Using an electric actuator as a power source, automated operation can be achieved through an electrical control system, improving work efficiency, reducing manual intervention, and lowering the risk of manual misoperation.
2. Precise control: The electric actuator has high-precision position control capabilities, accurately controlling the opening and closing state of the valve core to ensure the cut-off and passage effects of pipeline fluids, improving equipment stability and reliability.
3. Multiple control methods: Electric gate valves can adopt various control methods as needed, such as manual control, remote control, and remote monitoring, to meet the control requirements of different scenarios.
4. High sealing performance: Electric gate valves use high-quality sealing structures and materials, with good sealing performance, effectively preventing fluid leakage and the intrusion of external pollutants, ensuring the safety and cleanliness of the pipeline system.
5. High-pressure and corrosion resistance: The material selection and processing technology of electric gate valves have undergone strict screening and can adapt to various operating environments, with high-pressure and corrosion-resistant characteristics, suitable for controlling various liquid and gas media.
Keyword:




